
Programme
Introduction and welcome
South Africa is home to more than 10 million young people between the ages of 15 to 24. This youth
cohort constitutes 19% of the total population.4 In 2011, more than six out of 10 young people (62%)
aged 15 –24 lived in households with a per capita monthly income of less than R779 [the “upper bound
poverty line”5] compared to 46% of the adult population.
Purpose and expectations
Background overview and context
The context
What is the status of youth in Sekororo?
What is the difference between income generation and employment
Employment and income generation are related concepts but differ in their scope and nature:
1.Employment:
•Definition: Employment refers to having a job, occupation, or work in exchange for
payment, usually in the form of wages or salary.
•Nature: Employment typically involves working for an employer, whether in the public
or private sector, and often includes benefits such as social security, health insurance,
and paid leave.
•Examples: Working as a teacher, nurse, factory worker, or office employee are examples
of employment.
2.Income Generation:
•Definition: Income generation refers to the process of creating or earning income
through various activities, which may or may not involve traditional employment.
•Nature: Income generation activities can range from traditional employment to
entrepreneurial ventures, freelance work, and other forms of self-employment.
•Examples: Starting a small business, selling handmade crafts, offering freelance services,
or farming for profit are examples of income generation activities.

Activities:
Activity XXX
a)Plenary: agree or disagree
i)In this session the youth group will agree or disagree with controversial statements affecting
youth income generation challenges and opportunities
•Young people from Sekororo are all lazy. That is why they are not involved in the
local economy
•Youth do not have access to start up capital therefore they cannot enter the formal
or informal economy
•The social grant system is making the youth dependent
•The child income grant is encouraging the youth to have children and not seek
income generation opportunity
•The education system does not prepare youth for the future especially self
employment
•There are no good examples of small business development in rurual areas
•The challenge is distance to markets
Activity xxx
2)Group work
Activities conducted as 4 groups:
a)Order income generation activities: look at pictures in your group and order from most
accessible to least accessible in rural villages
Discussion:
1.Conservation: Raise awareness about environmental issues and the importance of conservation
through educational sessions, clean-up campaigns, and tree-planting activities.
2.Tourism: work in the tourism sector: catering, hospitality, rangers, guides, craft manufacture,
health and beauty
3.Cultural activities: to promote understanding and appreciation of different cultures, traditions,
and perspectives for diverse backgrounds. Music, medicine, craft, dress, makeup etc
4.Health and Wellness: Offer workshops on nutrition, exercise, mental health,
5.Sports Tournaments and Fitness Challenges: Arrange sports tournaments and fitness challenges
to promote physical activity, teamwork, and healthy competitions with sponsorship.
6.Creative Arts Workshops: Provide workshops on various local art forms

Activity XX
Top ten challenges for new income generation activities: create cards for challenges then place them in
the order from most to least challenging in rural Sekororo
Report back
Discussion
Activity XXX
Monetizing an item or skill means finding a way to make money from it. For example, if you have a skill
like cooking, you might monetize it by starting a catering business or offering cooking classes. Similarly,
if you have an item like a piece of land, you might monetize it by renting it out or using it for farming to
generate income. Essentially, monetizing means turning something you have into a source of income.
3)Monetising an item: You will be provided with an item. Discuss in your group
•what income generation opportunities it can be associated with
•What will be required to create value around this item
•Who will be necessary in your network to make this business function
•What kind of income you will receive
•How many people you would need to have on your team.
Discussion
Monetising in the context of rural development and income generation refers to the process of
converting a non-monetary asset or activity into a source of income or revenue. This can involve various
strategies and approaches, such as:
1.Product or Service Development: Creating products or services that can be sold or traded in the
market. For example, turning agricultural produce into goods for sale, such as processed foods
or handicrafts.
2.Digital Skills: training on digital literacy, including basic computer skills, internet usage, and
online safety, to enhance youth's access to information and opportunities in the digital age.
3.Value Addition: Adding value to existing products or services to increase their market value.
This can include packaging, branding, or improving the quality of the product.
4.Market Access: Identifying and accessing markets where products or services can be sold
profitably. This may involve exploring local, regional, or even international markets.
5.Financial Management: Managing finances effectively to ensure that income generated is
reinvested or saved for future growth and sustainability.
6.Diversification: Diversifying income sources to reduce reliance on a single source of income.
This can involve exploring multiple income-generating activities or ventures.
7.Networking and Collaboration: Building networks and partnerships with other businesses,
organizations, or stakeholders to access resources, markets, or expertise.
Stepsin the process
Monetizing an item or skill in rural development means finding ways to make money from it. This
includes:
1.Finding Ways to Make Money: Figuring out how the item or resource can be used to generate
income.
2.Making a Plan: Creating a plan to turn the item or resource into income. This might involve
creating new products or services, finding new markets, or working with other businesses.
3.Putting the Plan into Action: Taking steps to make the plan happen. This could include creating
and selling new products or services, promoting them to customers, and managing the money
earned.
4.Reviewing and Adjusting: Continuously checking to see if the plan is working and making
changes if needed. This might involve improving products or services, finding new markets, or
trying new ways to make money.
Activity XXX
Support networks: list all the organisations, government departments, NGOS, groups, businesses that
can provide advice, support, finances for small business start ups
Discussion
Networking and collaborating with others can help rural villages make money from their resources and
skills. Here's how:
1.Getting to More Customers: Working with local businesses or groups can help sell more
products or services.
2.Sharing Things: Sharing tools, buildings, or skills with others can save money and make things
easier.
3.Learning from Others: Talking to experts or groups can help learn about what people want to
buy and how to do things better.

4.Getting Help and Advice: Getting help and advice from people who know what they're doing
can make it easier to start a business.
5.Working Together: Doing projects or starting businesses with others can help everyone do
better and make more money.
6.Getting Support:Talking to government or groups can help get money, training, or other help
for starting a business.
7.Getting the Community Involved: Getting everyone in the community excited and involved can
help businesses grow and be more successful.
Report back
Innovation is key
Here are some examples of innovation:
1.Technology: The development of smartphones and mobile apps revolutionized communication
and access to information.
2.Healthcare:The invention of vaccines and antibiotics has significantly reduced the impact of
diseases and saved millions of lives.
3.Transportation: The introduction of electric cars and self-driving technology is changing the way
we travel and reducing our impact on the environment.
4.Entertainment: Streaming services like Netflix have transformed how we consume media,
making it more convenient and personalized.
5.Education: Online learning platforms have made education more accessible and flexible,
allowing people to learn anytime, anywhere.
6.Finance: The rise of fintech companies and digital payment systems has made banking and
financial services more efficient and inclusive.
7.Energy: The development of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power is reducing
our dependence on fossil fuels and combating climate change
Innovation in rural areas.
Here are some examples:
1.Agricultural Innovation: Introducing new farming techniques, crop varieties, or technologies
(such as precision agriculture or hydroponics) can improve crop yields, reduce water usage, and
increase farm profitability.
2.Rural Healthcare Innovation: Implementing telemedicine services or mobile health clinics can
improve access to healthcare in remote areas, while innovations in medical technology can
improve diagnosis and treatment options.
3.Rural Entrepreneurship: Supporting and encouraging entrepreneurship in rural areas can lead
to the creation of new businesses and industries, providing employment opportunities and
stimulating economic growth.
4.Renewable Energy Innovation: Implementing renewable energy solutions such as solar panels
or small-scale wind turbines can provide sustainable energy sources for rural communities,
reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
5.Digital Innovation: Improving access to high-speed internet and digital technologies can open
up new opportunities for education, communication, and business development in rural areas.
6.Infrastructure Innovation: Developing innovative solutions for transportation, water
management, and waste disposal can improve living conditions and quality of life in rural
communities.
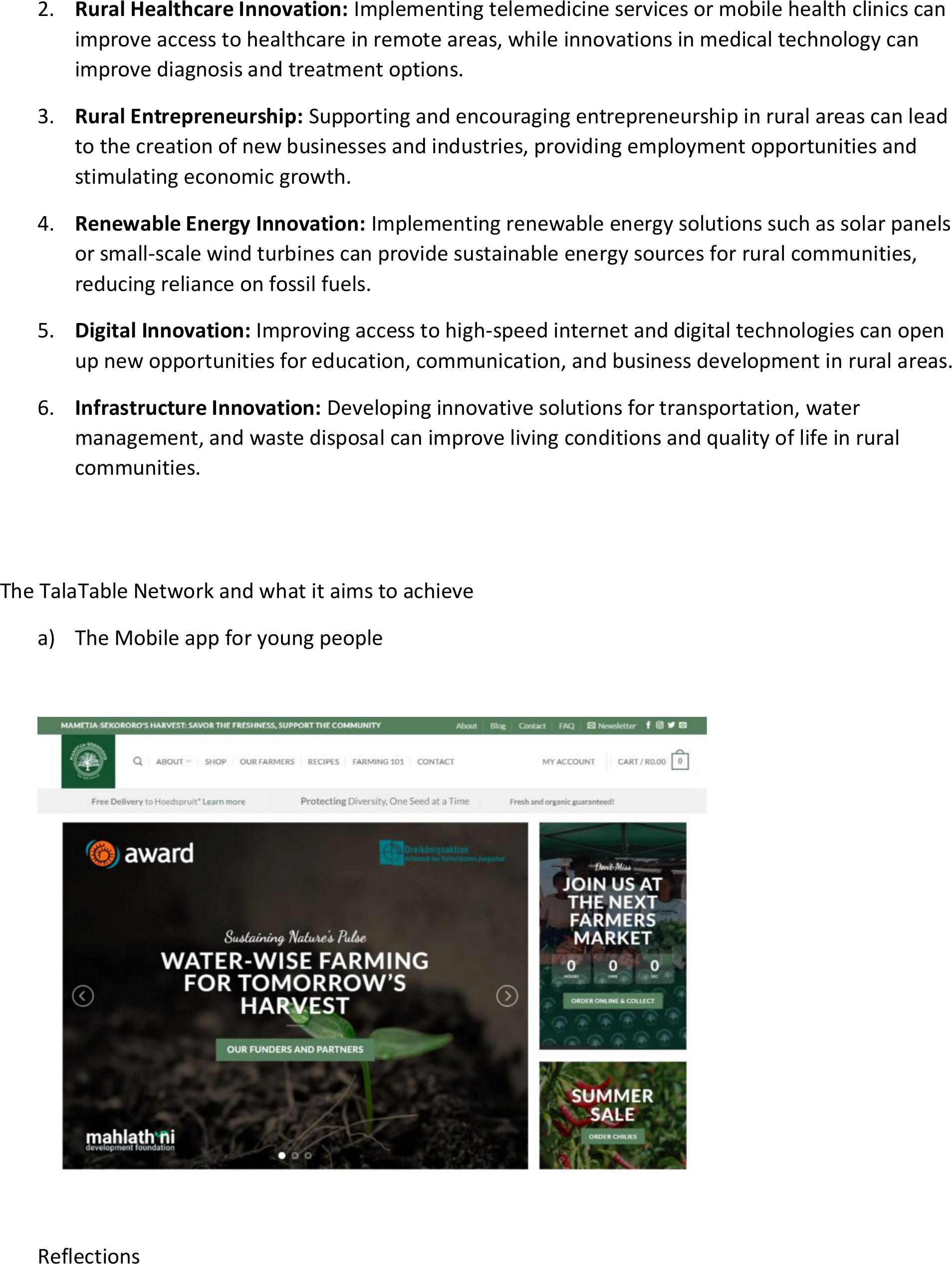
The TalaTable Network and what it aims to achieve
a)The Mobile app for young people
Reflections

Closure