
The impact of conservation agriculture on
maize ear rots and resultant mycotoxin
production in commercial and smallholder
farming systems
MTM 19/03
Dr.Belinda Jansevan Rensburg
BelindaJ@arc.agric.za

Background
•Does an increase in residue cause an increase in disease and
mycotoxins?
•Crop rotation is crucial, however maize residues take longer to
decompose
- harbor Fusarium and other ear rot pathogens much longer
•2019/20 – 2022/23

Aim
•Todeterminetheeffect
of agricultural cropping
systemsonmaize earrot
infection and mycotoxin
contaminationindiverse
production areas
(commercial and
smallholder farmers)

Where doesthefungicome from that produce
mycotoxins?
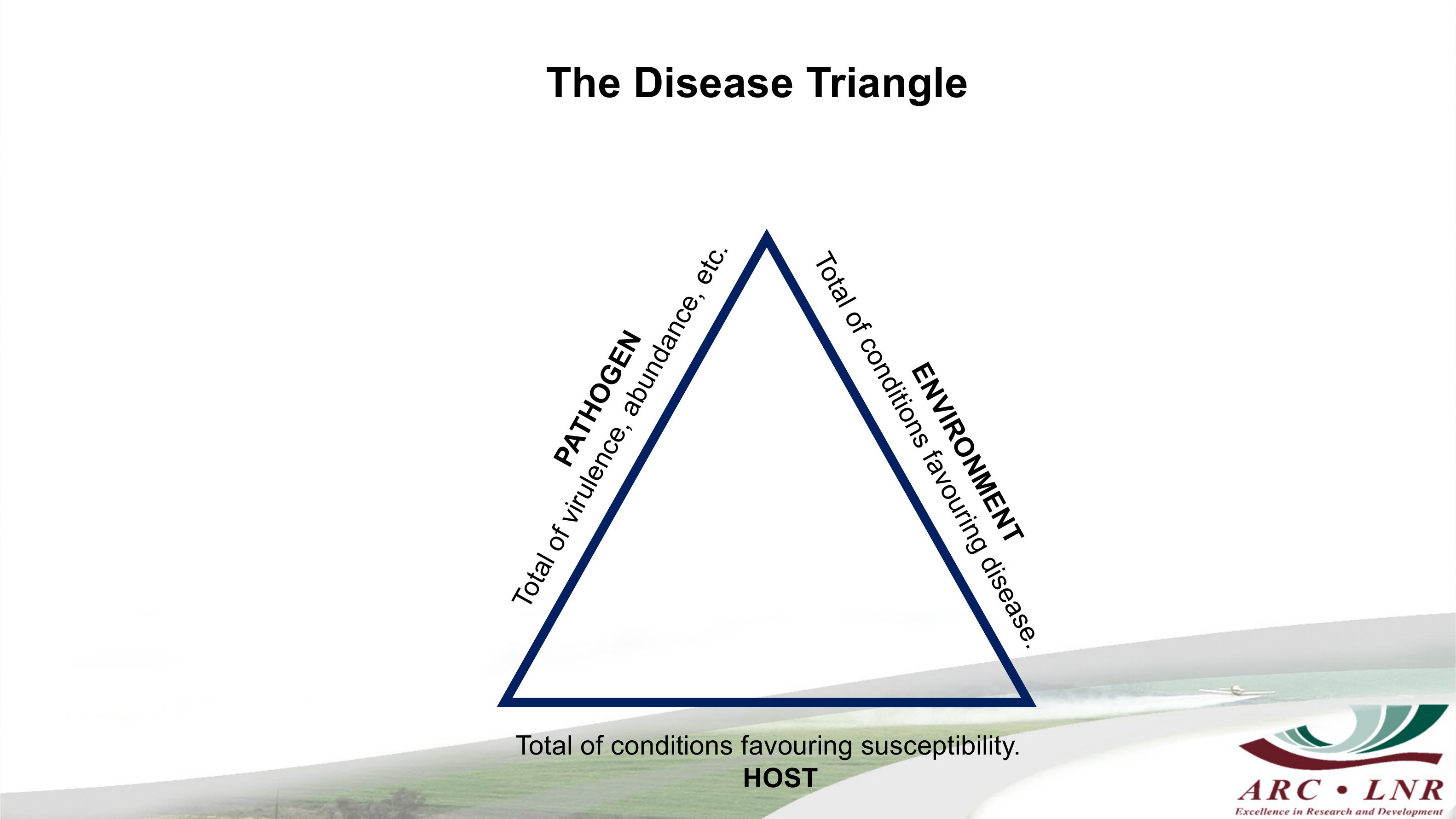
The Disease Triangle
PATHOGEN
Total of virulence, abundance, etc.
ENVIRONMENT
Total of conditions favouring disease.
Total of conditions favouring susceptibility.
HOST
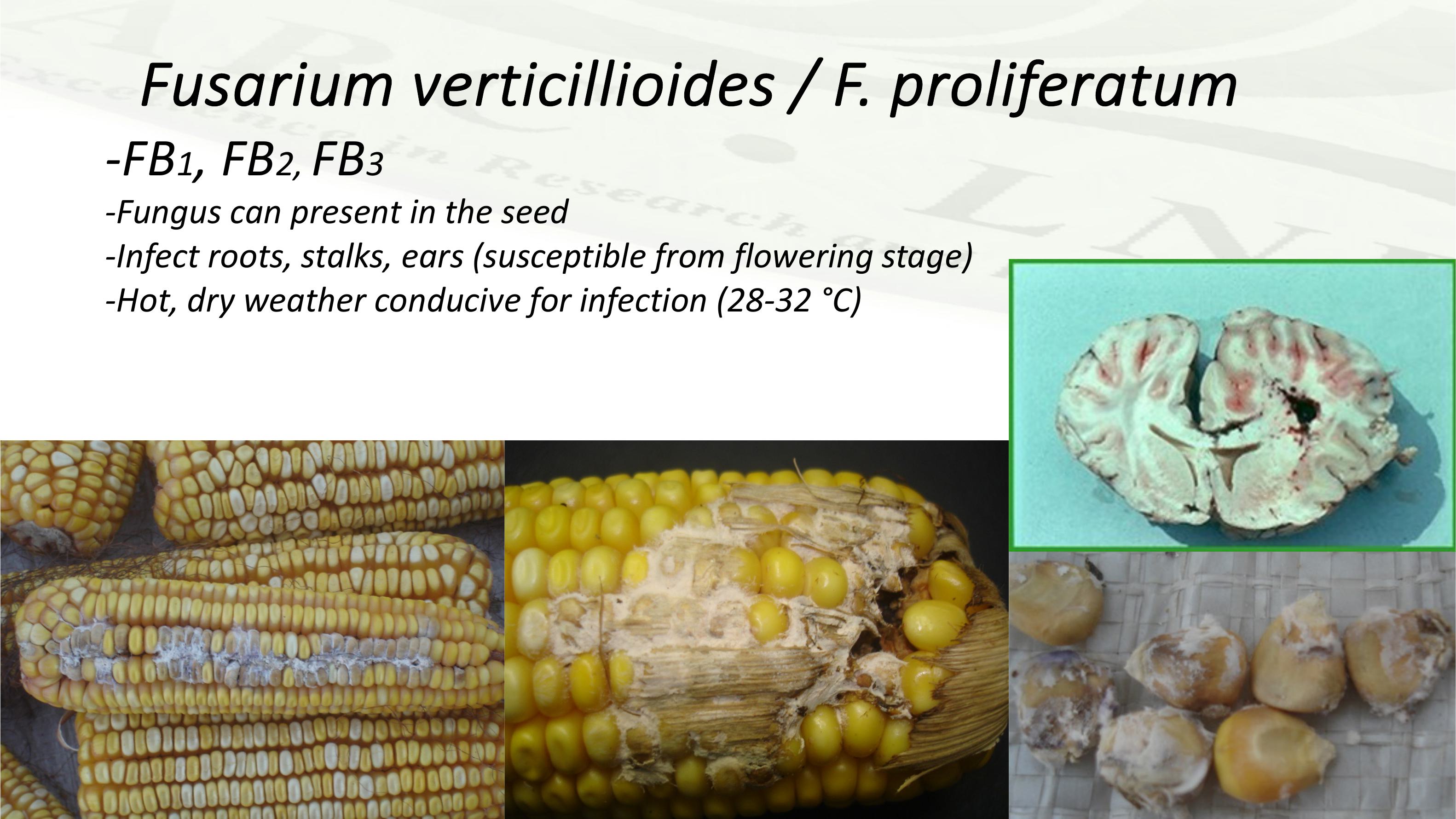
Fusariumverticillioides/ F. proliferatum
-FB1, FB2, FB3
-Funguscanpresent intheseed
-Infect roots, stalks, ears (susceptible from flowering stage)
-Hot, dry weather conducive for infection (28-32 °C)

Fusariumgraminearum spp. complex
-DON, NIV, ZEA
-Funguscanpresent intheseed
-Infect roots, stalks, ears (susceptible from flowering stage)
-Hot, wet weather conducive for infection (25-32 °C)

Stenocarpellamaydis
-Diplodiatoxin, Dipmatol
-diplodiosis, a neuromycotoxicosisof cattle and sheep
-Maize is the only host
-Start at the base of the maize ear, grow upward
-Late season rains, “skelm” Diplodia
M.G. Masango, B.C. Flett, C.E. Ellisand C.J. Botha.Stenocarpellamaydisand its toxic metabolites: a South African perspective on
diplodiosis. World Mycotoxin Journal, 2015; 8 (3): 341-350 WageningenAcademic Publishers.

Whymust we managemycotoxins?
•Affect the entire food and feed production chain.
•Reductionofmarketablegrain,increasedcostofdrying, decreasedweight
gaininanimalfeeding,fertilityproblems,andincreasedcostsforanimal
and human health.
•Restrictmarkets(fordevelopingcountries)

Materials and Methods
•Commercial farmers (2019/20 – 2022/23)
•Ottosdal, Kroonstad, Makwassie, Reitz
•56 samples collected before harvest
- different CA farming practices
•GPS – Fields area measure app
•Smallholder farmers (2019/20 – 2022/23)
•Bergville, Southern KZN, Midlands
•77 samples collected before harvest
- different CA farming practices
•individual samples sent to SAGL for multi –mycotoxin analyses
•Milled samples – DNA extractions, qPCR

Results– Commercial farmers

Table 1: Experimentaldesignincludingmaizemonoculture,croprotations,twodifferentrowwidthsand
plantdensities,repeatedthreetimesover a three-yeartimeperiod (Ottosdaltrialonly).
Maize50=rowwidth50cmandplantdensity =40 000ha-1
2018
/19
2019
/20
2020
/21
2021
/22
Block
1
Maize
50*
Maize
90
Maize
50
Maize
90
Maize
50
Maize
90
Maize
50
Maize
90
Maize
50
Maize
90
Sunflower
Cover
crop
Maize
50
Maize
90
Cover
crop
Maize
50
Maize
90
Sunflower
Cover
crop
Block
2
Maize
50
Maize
90
Maize
50
Maize
90
Maize
50
Maize
90
Maize
50
Maize
90
Maize
50
Maize
90
Sunflower
Cover
crop
Maize
50
Maize
90
Cover
crop
Maize
50
Maize
90
Sunflower
Cover
crop
Block
3
Maize
50
Maize
90
Maize
50
Maize
90
Maize
50
Maize
90
Maize
50
Maize
90
Maize
50
Maize
90
Sunflower
Cover
crop
Maize
50
Maize
90
Cover
crop
Maize
50
Maize
90
Sunflower
Cover
crop
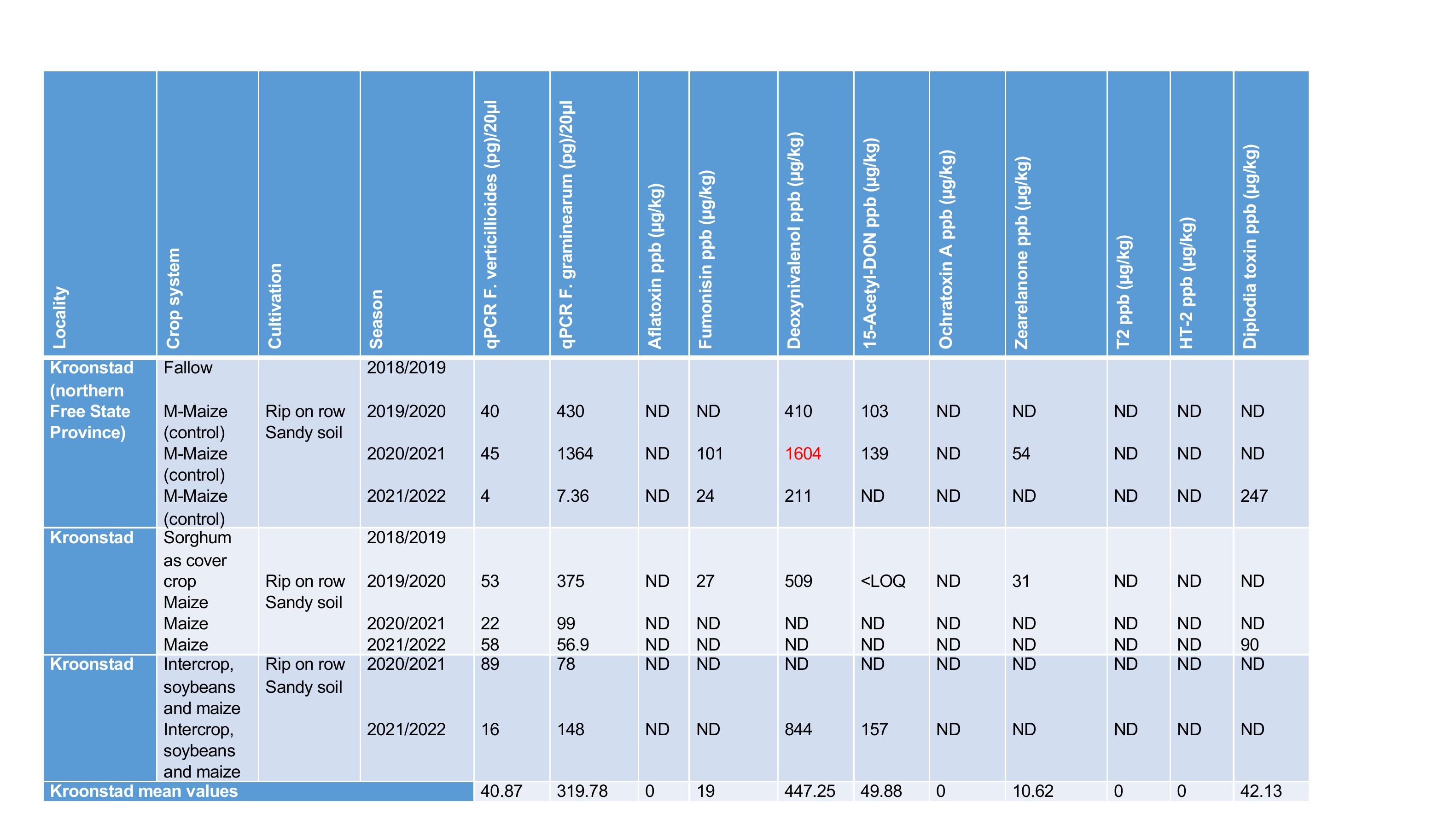
Locality
Crop system
Cultivation
Season
qPCR F. verticillioides (pg)/20µl
qPCR F. graminearum (pg)/20µl
Aflatoxin ppb (µg/kg)
Fumonisin ppb (µg/kg)
Deoxynivalenol ppb (µg/kg)
15
-Acetyl-DON ppb (µg/kg)
Ochratoxin A ppb (µg/kg)
Zearelanone ppb (µg/kg)
T2 ppb (µg/kg)
HT
-2 ppb (µg/kg)
Diplodia toxin ppb (µg/kg)
Kroonstad
(northern
Free State
Province)
Fallow
M
-Maize
(control)
M
-Maize
(control)
M
-Maize
(control)
Rip on row
Sandy soil
2018/2019
2019/2020
2020/2021
2021/2022
40
45
4
430
1364
7.36
ND
ND
ND
ND
101
24
410
1604
211
103
139
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
54
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
247
Kroonstad
Sorghum
as cover
crop
Maize
Maize
Maize
Rip on row
Sandy soil
2018/2019
2019/2020
2020/2021
2021/2022
53
22
58
375
99
56.9
ND
ND
ND
27
ND
ND
509
ND
ND
<LOQ
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
31
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
90
Kroonstad
Intercrop,
soybeans
and maize
Intercrop,
soybeans
and maize
Rip on row
Sandy soil
2020/2021
2021/2022
89
16
78
148
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
844
ND
157
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Kroonstad mean values
40.87
319.78
0
19
447.25
49.88
0
10.62
0
0
42.13
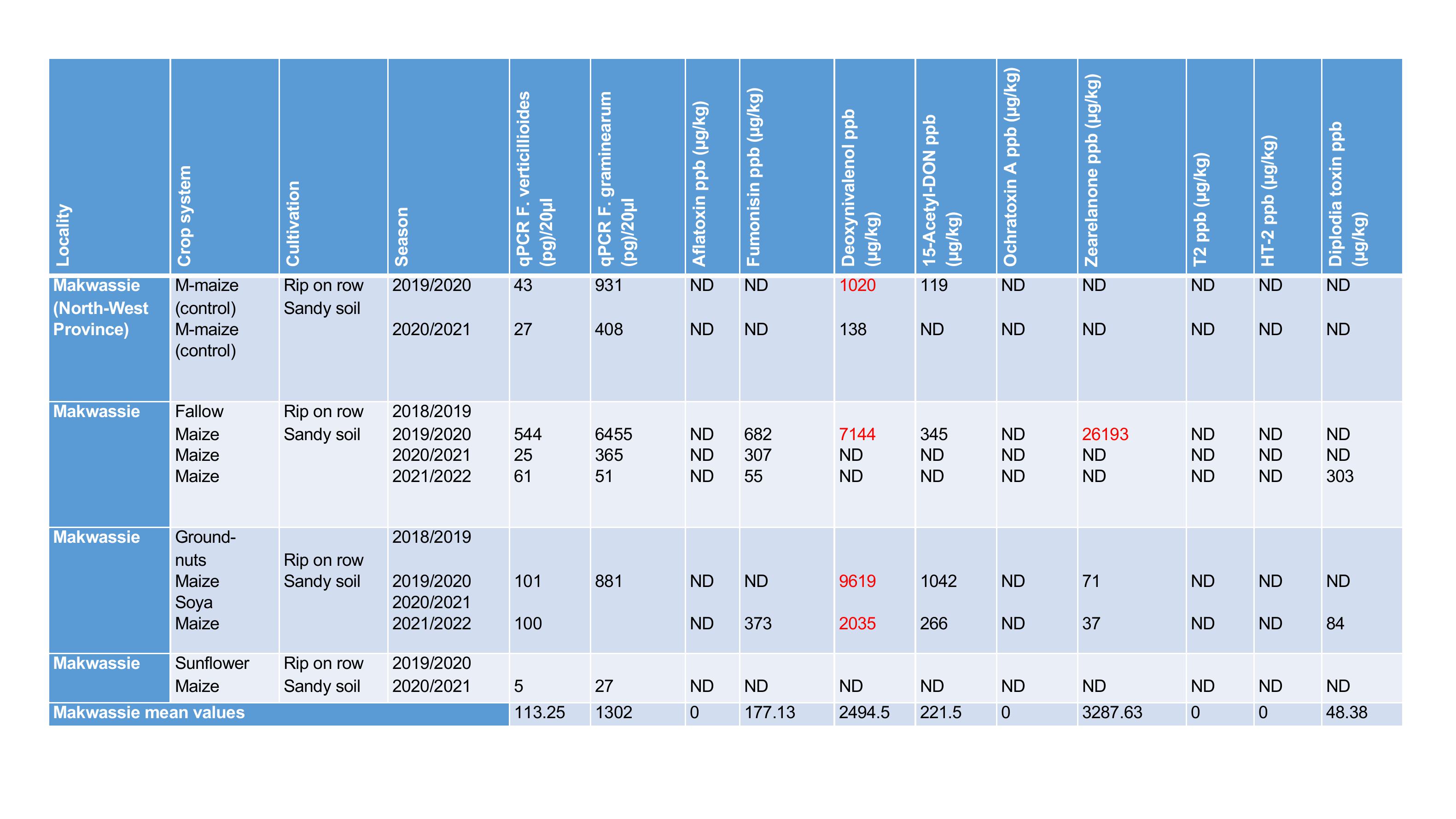
Locality
Crop system
Cultivation
Season
qPCR F. verticillioides
(
pg)/20µl
qPCR F.
graminearum
(
pg)/20µl
Aflatoxin ppb (µg/kg)
Fumonisin
ppb (µg/kg)
Deoxynivalenol ppb
(µg/kg)
15
-Acetyl-DON ppb
(µg/kg)
Ochratoxin A ppb (µg/kg)
Zearelanone
ppb (µg/kg)
T2 ppb (µg/kg)
HT
-2 ppb (µg/kg)
Diplodia
toxin ppb
(µg/kg)
Makwassie
(North
-West
Province)
M
-maize
(control)
M
-maize
(control)
Rip on row
Sandy soil
2019/2020
2020/2021
43
27
931
408
ND
ND
ND
ND
1020
138
119
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Makwassie
Fallow
Maize
Maize
Maize
Rip on row
Sandy soil
2018/2019
2019/2020
2020/2021
2021/2022
544
25
61
6455
365
51
ND
ND
ND
682
307
55
7144
ND
ND
345
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
26193
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
303
Makwassie
Ground
-
nuts
Maize
Soya
Maize
Rip on row
Sandy soil
2018/2019
2019/2020
2020/2021
2021/2022
101
100
881
ND
ND
ND
373
9619
2035
1042
266
ND
ND
71
37
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
84
Makwassie
Sunflower
Maize
Rip on row
Sandy soil
2019/2020
2020/2021
5
27
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Makwassie mean values
113.25
1302
0
177.13
2494.5
221.5
0
3287.63
0
0
48.38
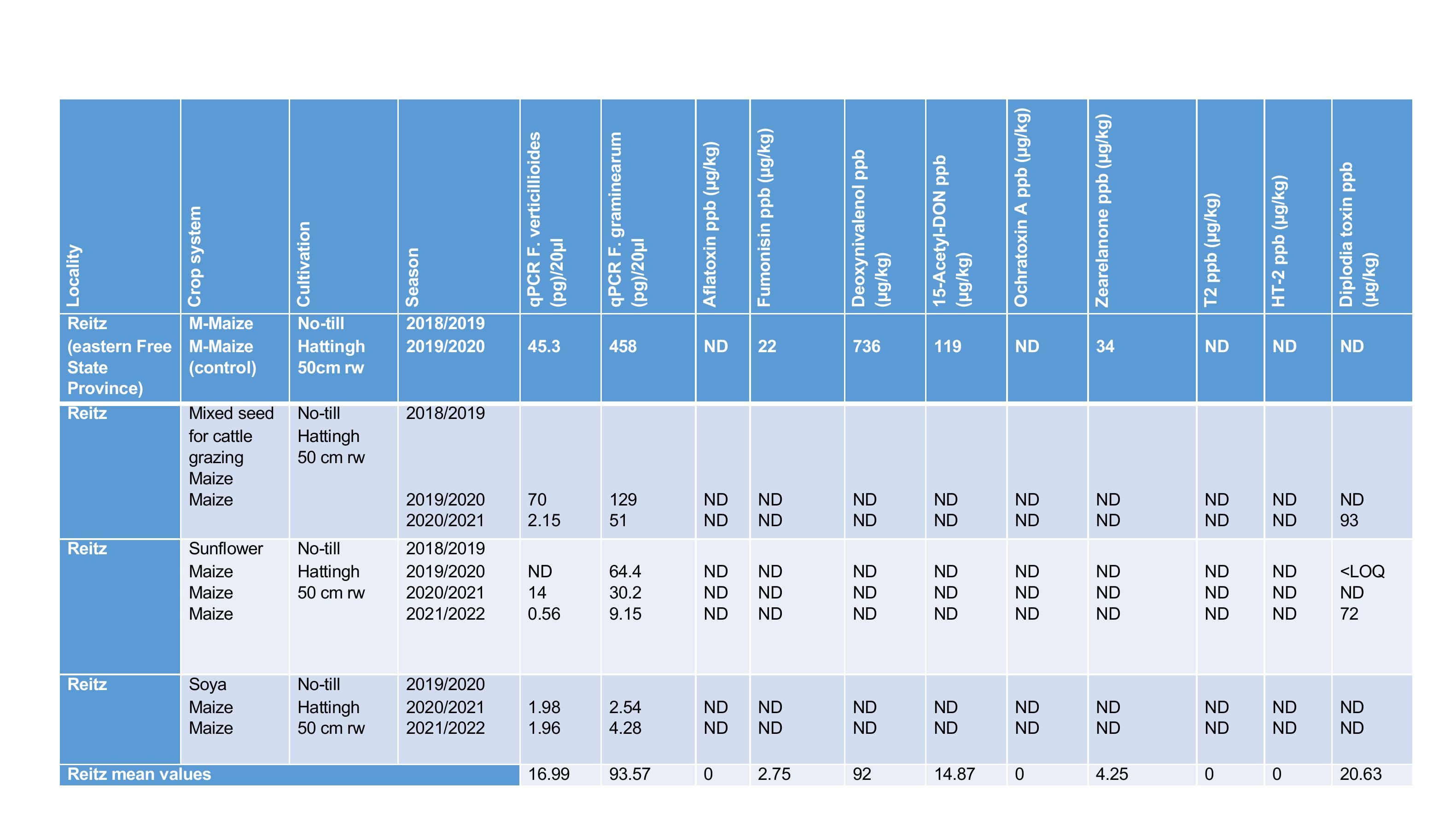
Locality
Crop system
Cultivation
Season
qPCR F. verticillioides
(
pg)/20µl
qPCR F.
graminearum
(
pg)/20µl
Aflatoxin ppb (µg/kg)
Fumonisin
ppb (µg/kg)
Deoxynivalenol ppb
(µg/kg)
15
-Acetyl-DON ppb
(µg/kg)
Ochratoxin A ppb (µg/kg)
Zearelanone
ppb (µg/kg)
T2 ppb (µg/kg)
HT
-2 ppb (µg/kg)
Diplodia
toxin ppb
(µg/kg)
Reitz
(eastern Free
State
Province)
M
-Maize
M
-Maize
(control)
No
-till
Hattingh
50cm rw
2018/2019
2019/2020
45.3
458
ND
22
736
119
ND
34
ND
ND
ND
Reitz
Mixed seed
for cattle
grazing
Maize
Maize
No
-till
Hattingh
50 cm
rw
2018/2019
2019/2020
2020/2021
70
2.15
129
51
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
93
Reitz
Sunflower
Maize
Maize
Maize
No
-till
Hattingh
50 cm rw
2018/2019
2019/2020
2020/2021
2021/2022
ND
14
0.56
64.4
30.2
9.15
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
<LOQ
ND
72
Reitz
Soya
Maize
Maize
No
-till
Hattingh
50 cm rw
2019/2020
2020/2021
2021/2022
1.98
1.96
2.54
4.28
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Reitz mean values
16.99
93.57
0
2.75
92
14.87
0
4.25
0
0
20.63
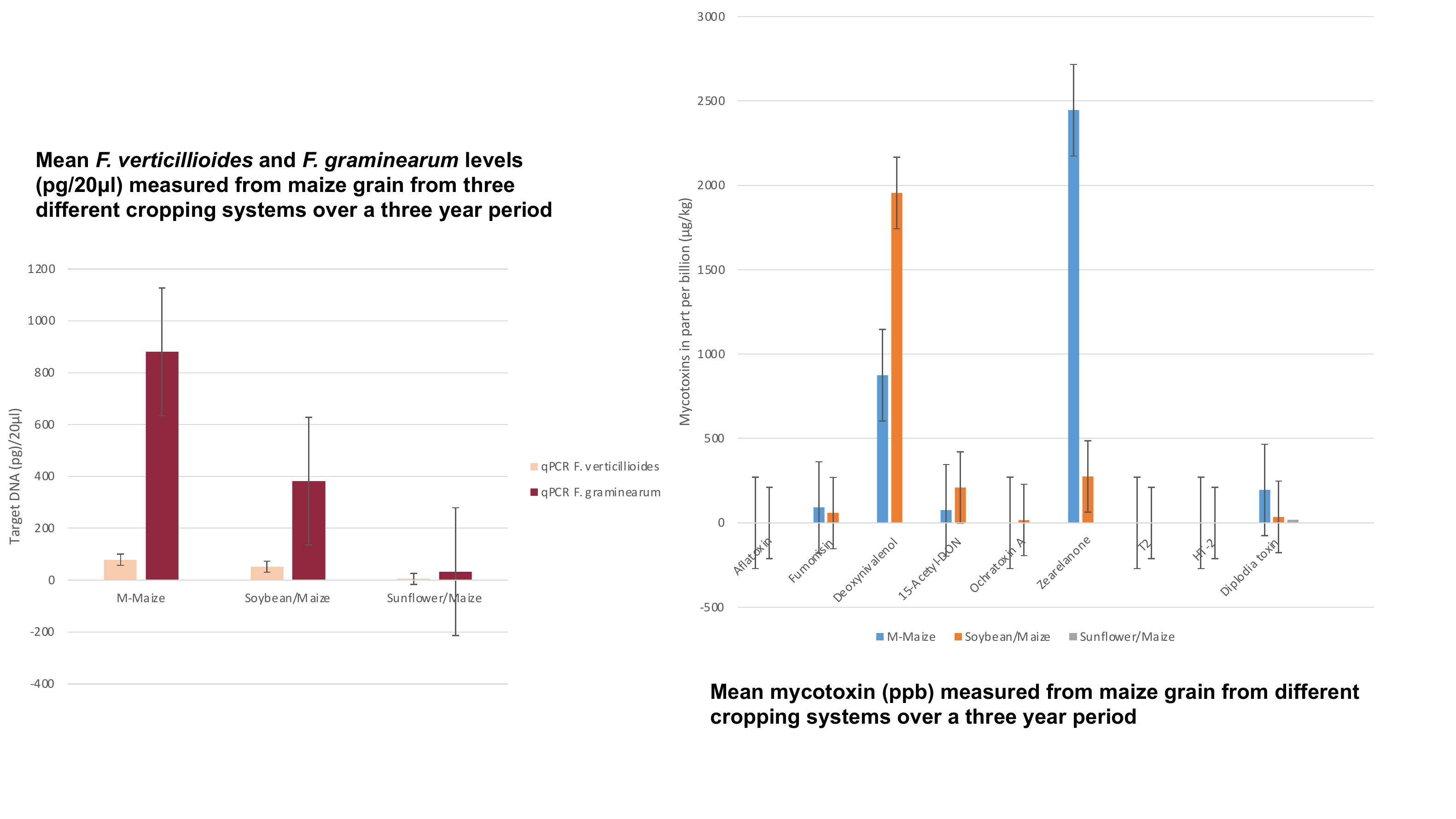
Mean F.verticillioidesand F.graminearumlevels
(pg/20µl) measured from maize grain from three
different cropping systems over a three year period
-400
-200
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
M-Maize Soybe an /MaizeSunflowe r/Ma iz e
Target DNA (pg)/20µl)
qPCR F. verticillioides
qPCR F. graminearum
-500
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
Aflatox in
Fumonisin
De o xyn ival en o l
15-Acetyl-DON
Ochratoxin A
Ze ar elan on e
T2
HT -2
Diplodia toxin
Mycotoxins in part per billion (µg/kg)
M-Maize Soybe an /MaizeSunflowe r/Ma iz e
Mean mycotoxin (ppb) measured from maize grain from different
cropping systems over a three year period

Results– Smallholder farmers
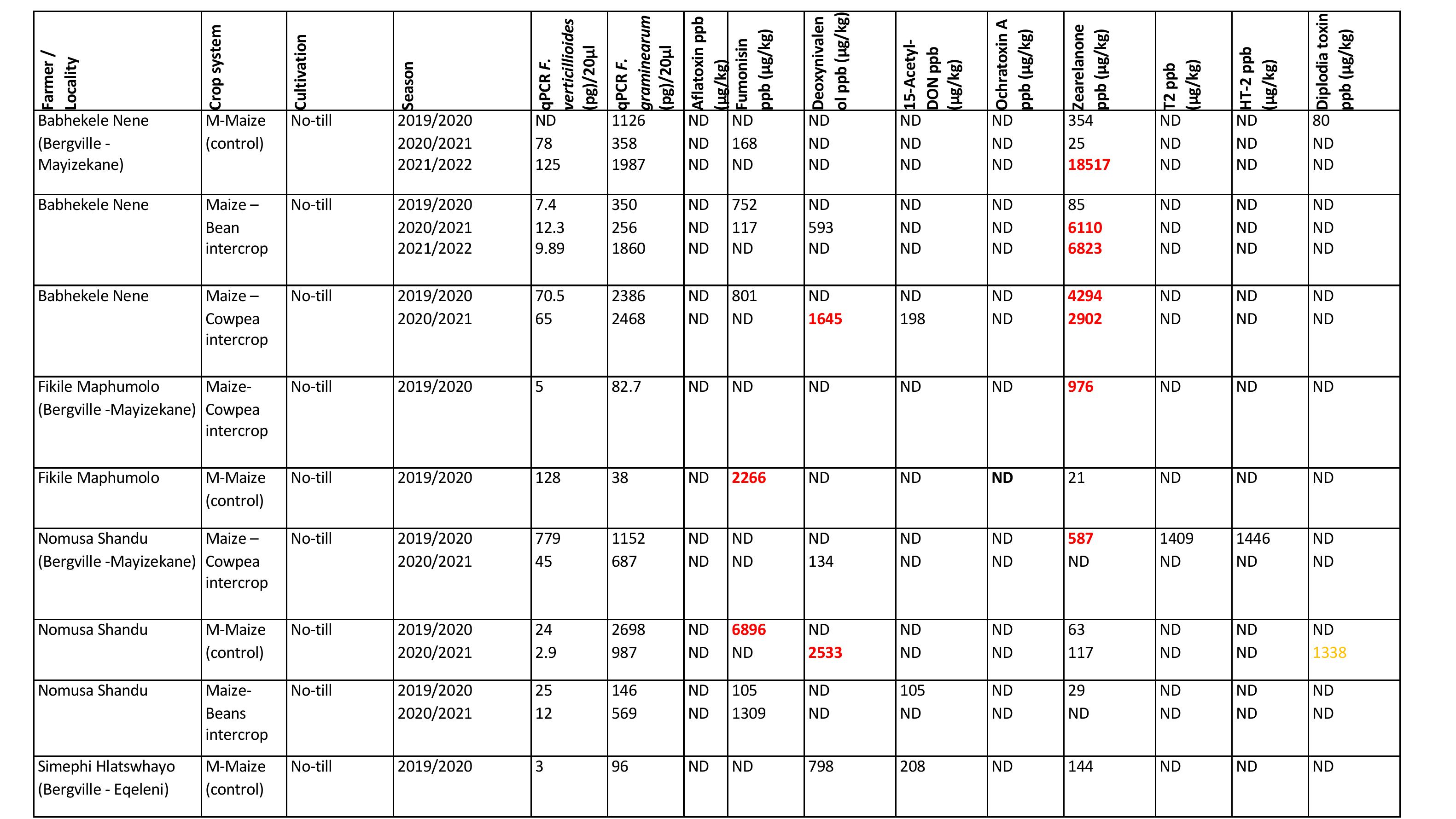
Farmer /
Locality
Crop system
Cultivation
Season
qPCR
F.
verticillioides
(pg)/20µl
qPCR
F.
graminearum
(pg)/20µl
Aflatoxin ppb
(µg/kg)
Fumonisin
ppb (µg/kg)
Deoxynivalen
ol ppb (µg/kg)
15
-Acetyl-
DON ppb
(µg/kg)
Ochratoxin A
ppb (µg/kg)
Zearelanone
ppb (µg/kg)
T2 ppb
(µg/kg)
HT
-2 ppb
(µg/kg)
Diplodia toxin
ppb (µg/kg)
Babhekele Nene
(Bergville
-
Mayizekane)
M
-Maize
(control)
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
2021/2022
ND
78
125
1126
358
1987
ND
ND
ND
ND
168
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
354
25
18517
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
80
ND
ND
Babhekele Nene
Maize
–
Bean
intercrop
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
2021/2022
7.4
12.3
9.89
350
256
1860
ND
ND
ND
752
117
ND
ND
593
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
85
6110
6823
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Babhekele Nene
Maize
–
Cowpea
intercrop
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
70.5
65
2386
2468
ND
ND
801
ND
ND
1645
ND
198
ND
ND
4294
2902
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Fikile Maphumolo
(Bergville
-
Mayizekane)
Maize
-
Cowpea
intercrop
No
-till
2019/2020
5
82.7
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
976
ND
ND
ND
Fikile Maphumolo
M
-Maize
(control)
No
-till
2019/2020
128
38
ND
2266
ND
ND
ND
21
ND
ND
ND
Nomusa Shandu
(Bergville
-
Mayizekane)
Maize
–
Cowpea
intercrop
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
779
45
1152
687
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
134
ND
ND
ND
ND
587
ND
1409
ND
1446
ND
ND
ND
Nomusa Shandu
M
-Maize
(control)
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
24
2.9
2698
987
ND
ND
6896
ND
ND
2533
ND
ND
ND
ND
63
117
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
1338
Nomusa Shandu
Maize
-
Beans
intercrop
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
25
12
146
569
ND
ND
105
1309
ND
ND
105
ND
ND
ND
29
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Simephi Hlatswhayo
(Bergville
- Eqeleni)
M
-Maize
(control)
No
-till
2019/2020
3
96
ND
ND
798
208
ND
144
ND
ND
ND
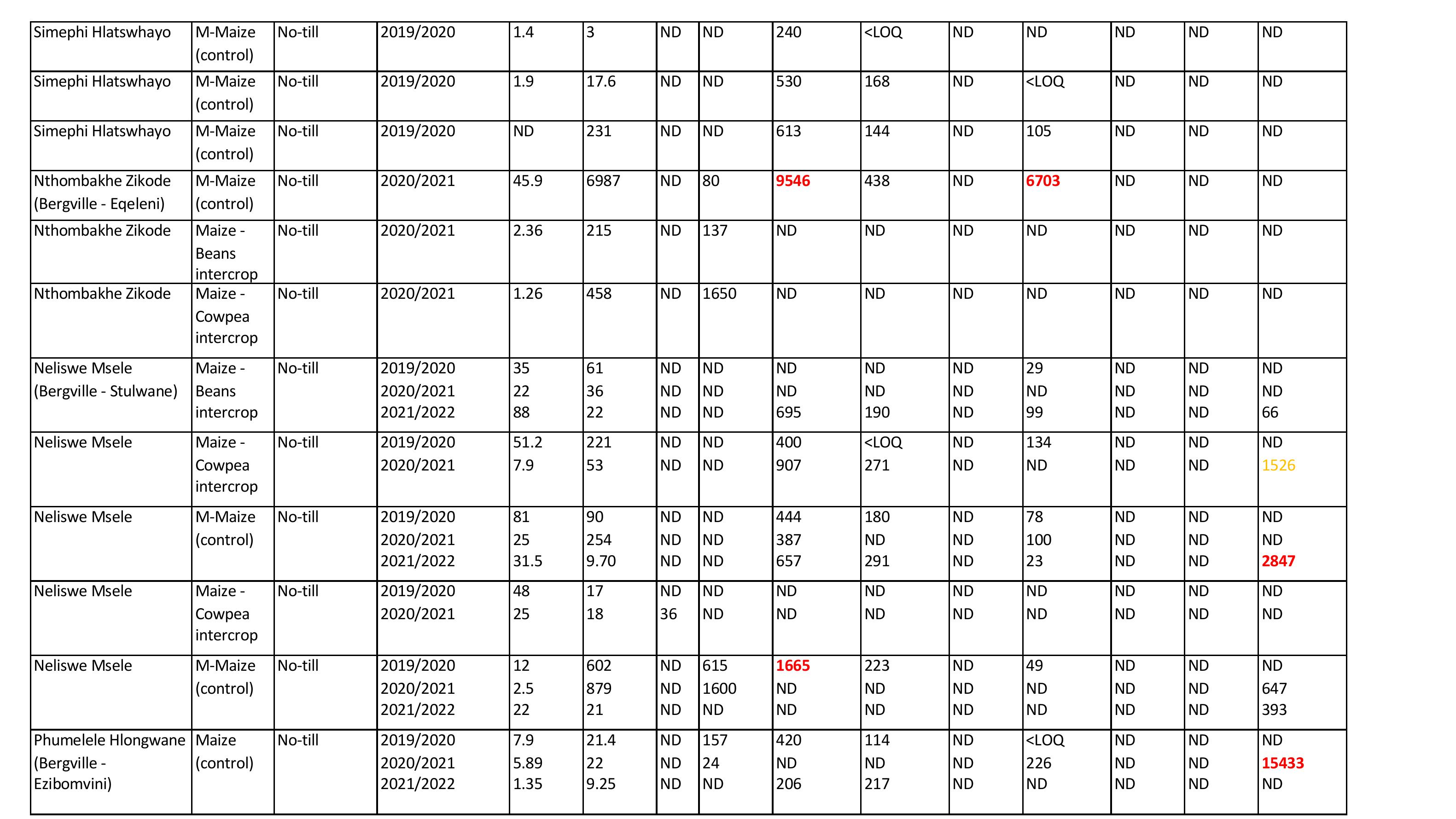
Simephi
Hlatswhayo
M
-Maize
(control)
No
-till
2019/2020
1.4
3
ND
ND
240
<LOQ
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Simephi
Hlatswhayo
M
-Maize
(control)
No
-till
2019/2020
1.9
17.6
ND
ND
530
168
ND
<LOQ
ND
ND
ND
Simephi Hlatswhayo
M
-Maize
(control)
No
-till
2019/2020
ND
231
ND
ND
613
144
ND
105
ND
ND
ND
Nthombakhe Zikode
(Bergville
- Eqeleni)
M
-Maize
(control)
No
-till
2020/2021
45.9
6987
ND
80
9546
438
ND
6703
ND
ND
ND
Nthombakhe Zikode
Maize
-
Beans
intercrop
No
-till
2020/2021
2.36
215
ND
137
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Nthombakhe Zikode
Maize
-
Cowpea
intercrop
No
-till
2020/2021
1.26
458
ND
1650
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Neliswe Msele
(Bergville
- Stulwane)
Maize
-
Beans
intercrop
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
2021/2022
35
22
88
61
36
22
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
695
ND
ND
190
ND
ND
ND
29
ND
99
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
66
Neliswe Msele
Maize
-
Cowpea
intercrop
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
51.2
7.9
221
53
ND
ND
ND
ND
400
907
<LOQ
271
ND
ND
134
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
1526
Neliswe Msele
M
-Maize
(control)
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
2021/2022
81
25
31.5
90
254
9.70
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
444
387
657
180
ND
291
ND
ND
ND
78
100
23
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
2847
Neliswe Msele
Maize
-
Cowpea
intercrop
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
48
25
17
18
ND
36
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Neliswe Msele
M
-Maize
(control)
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
2021/2022
12
2.5
22
602
879
21
ND
ND
ND
615
1600
ND
1665
ND
ND
223
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
49
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
647
393
Phumelele Hlongwane
(Bergville
-
Ezibomvini)
Maize
(control)
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
2021/2022
7.9
5.89
1.35
21.4
22
9.25
ND
ND
ND
157
24
ND
420
ND
206
114
ND
217
ND
ND
ND
<LOQ
226
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
15433
ND

Phumelele
Hlongwane
Maize
-
Beans
intercrop
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
2021/2022
4.4
5.4
0.83
16.7
238
2.88
ND
ND
ND
ND
302
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Phumelele
Hlongwane
Maize
-
Beans
intercrop
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
2021/2022
ND
2.3
1.31
595
25
11.7
373
ND
ND
127
24
ND
ND
ND
129
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Phumelele
Hlongwane
Maize
(control)
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
17
125
85
698
ND
ND
234
5750
1950
1623
177
159
ND
ND
30
31
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
842
Phumelele
Hlongwane
Maize
-
cover
crop
No
-till
2019/2020
34
100
ND
240
1418
518
ND
107
ND
ND
ND
Sibongile Mpulo
(Bergville
-
Vimbukhalo)
Maize
(control)
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
1.3
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
27
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
12798
Sibongile Mpulo
Maize
(control)
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
35
ND
ND
ND
23
41
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Sibongile Mpulo
Maize
No
-till
2019/2020
3.3
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Sibongile Mpulo
Maize
-
Cowpea
intercrop
No
-till
2019/2020
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Sibongile Mpulo
Maize
-
Beans
intercrop
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
1.4
ND
2.4
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Sibongile Mpulo
Maize
-
Beans
intercrop
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
10.2
2.8
78
89
ND
ND
ND
ND
399
826
<LOQ
ND
ND
ND
ND
1099
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Letta Ngubo (SKZN
-
Springvalley)
Maize
-
Beans
intercrop
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
4.6
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Letta Ngubo
M
-Maize
(control)
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
134
ND
ND
ND
81
ND
<LOQ
2467
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
1646
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Zweni Ndaba
(Bergville
-
Emabunzini)
Maize
-
Beans
intercrop
No
-till
2019/2020
39
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
Lethiwe Zimba
(Ndunwana)
Maize
No
-till
2019/2020
4.8
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
56
ND
ND
ND
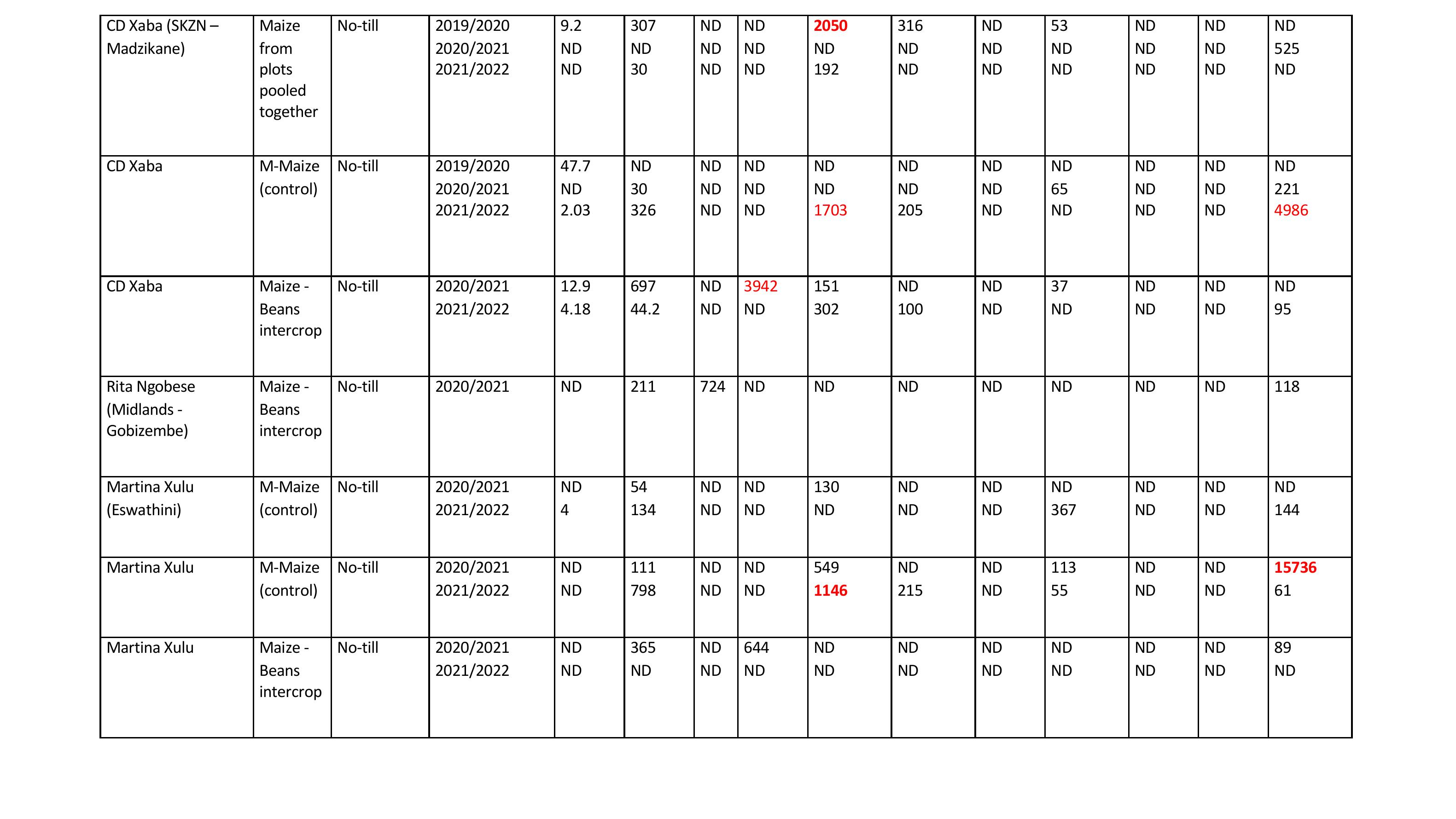
CD Xaba (SKZN
–
Madzikane)
Maize
from
plots
pooled
together
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
2021/2022
9.2
ND
ND
307
ND
30
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
2050
ND
192
316
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
53
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
525
ND
CD Xaba
M
-Maize
(control)
No
-till
2019/2020
2020/2021
2021/2022
47.7
ND
2.03
ND
30
326
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
1703
ND
ND
205
ND
ND
ND
ND
65
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
221
4986
CD Xaba
Maize
-
Beans
intercrop
No
-till
2020/2021
2021/2022
12.9
4.18
697
44.2
ND
ND
3942
ND
151
302
ND
100
ND
ND
37
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
95
Rita Ngobese
(Midlands
-
Gobizembe)
Maize
-
Beans
intercrop
No
-till
2020/2021
ND
211
724
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
118
MartinaXulu
(Eswathini)
M
-Maize
(control)
No
-till
2020/2021
2021/2022
ND
4
54
134
ND
ND
ND
ND
130
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
367
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
144
MartinaXulu
M
-Maize
(control)
No
-till
2020/2021
2021/2022
ND
ND
111
798
ND
ND
ND
ND
549
1146
ND
215
ND
ND
113
55
ND
ND
ND
ND
15736
61
MartinaXulu
Maize
-
Beans
intercrop
No
-till
2020/2021
2021/2022
ND
ND
365
ND
ND
ND
644
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
ND
89
ND

-100.00
0.00
100.00
200.00
300.00
400.00
500.00
600.00
700.00
800.00
900.00
M-MaizeMaize/Drybean Maize/Cowpea
qPCRF.verticillioidesqPCRF.graminearum
-1000
-500
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
Aflatoxin
Fumonisin
Deoxynivalenol
15-Acetyl-DON
Ochratoxin A
Zearelanone
T2
HT-2
Diplodia toxin
Mycotoxinsin ppb(µg/kg)
M-MaizeMaize/Drybean Maize/Cowpea
Mean F.verticillioidesand F.graminearumlevels (pg/20µl)
measured from maize grain from three different cropping
systems over a three year period.
Mean mycotoxins (ppb) measured from maize grain from different
cropping systems over a three year period.

Discussion
•Mycotoxin concentrations varied from one season to another
•Monoculture maize systems showed higher levels offungi and mycotoxins
•Visualcorrelationobservedbetweenamountoffungiandspecificmycotoxinsassociatedwithit
•Soybean and/or stubble may be a host for the F. graminearumspp. complex (commercial
farmers)
-Sunflower is a suitable rotation crop
•Maize/cowpea intercrop systems had higher F. ve rt i ci ll io id esand F. graminearuminfections
compared to
monoculture maize systems
•Cowpea produce minimal crop residues, but maybe a host for the F. graminearumspp. complex
(smallholder farmers)
-Dry beans is a suitable rotation crop
•Diplodiatoxinmeasured for the firsttime in SA– monoculture maize– smallholder farmers